Floats
Floats
A floating point number or float, depending on the language, is generally 32 bits / 4 bytes of machine code used to represent a signed (meaning including negative) decimal number. It gets it's name from the fact that after the sign bit, the next five bits are used to denote the exponent of the number or where the decimal point is, hence floating point. The significand is a sum of fractions where the first bit is
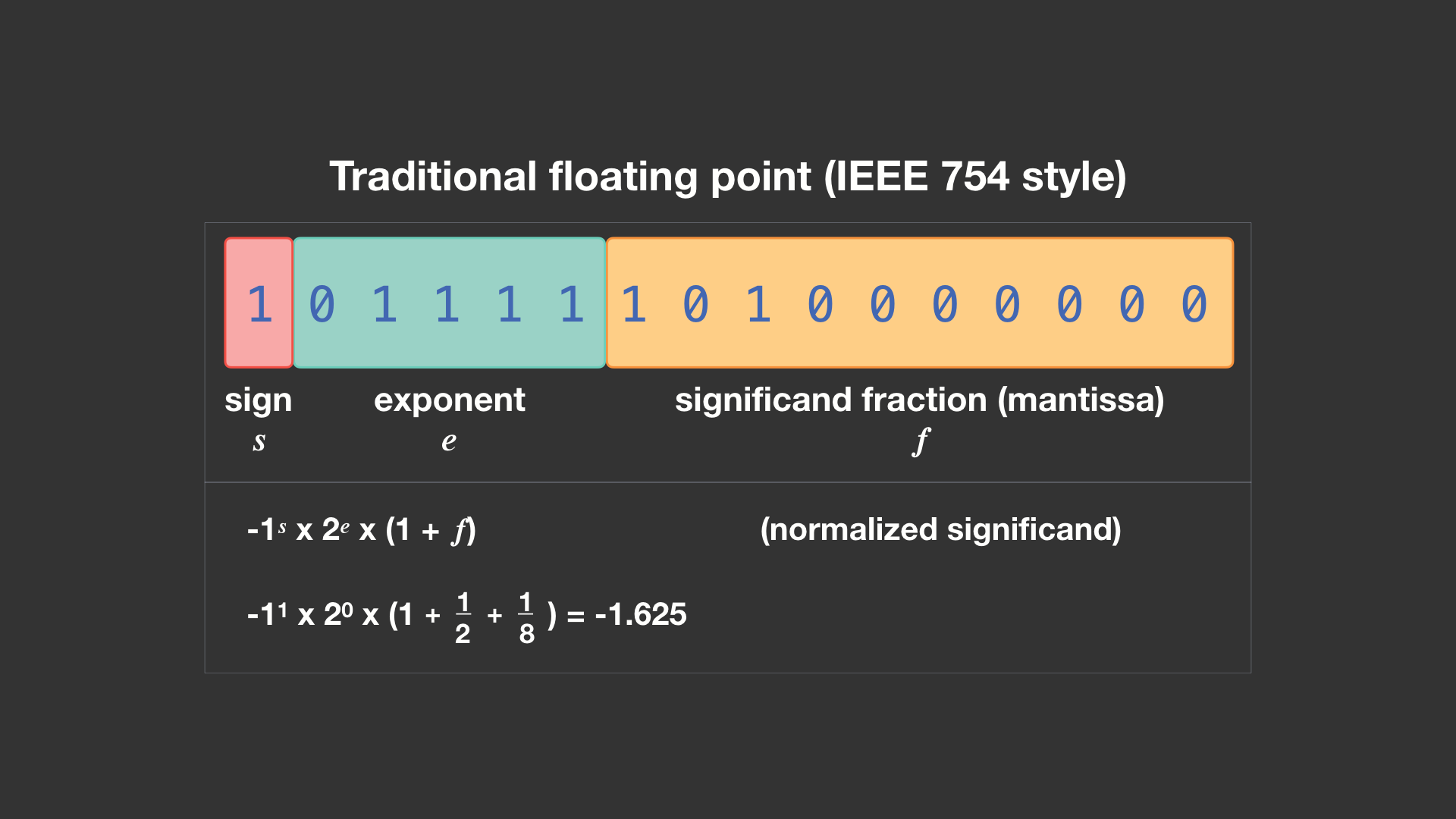
This way of storing numbers allows you to reach 7 decimal digits of precision within a massive range using only 32 bits / 4 bytes of memory.[1]
//These are valid integers (some languages use f suffix to denote floats)
float mols = 12.14f;
float avagadroConstant = 6.022E23f;
float boltzmannConstant = 1.380649f * Mathf.Pow(10, -23);
//These are invalid or inaccurate as they are not decimal values or are out of range
float plancksConstant = 6.62607015E-34f; //You lose 1 decimal digit of accuracy
float thisIsNotAFloat = "This is not a float";
For instance in C# and Java a float can represent values in the range:
float max = float.MaxValue;
float min = float.MinValue;
Console.WriteLine($"Range of float: {min} to {max}");
Range of float: -3.402823E+38 to 3.402823E+38
Because floats can be used to represent a massive range of values, it is better to think of them in terms of decimal digits of precision rather than in terms of size.
Doubles
When two floats love each other very much they combine like something out of an anime.
-Me
Basically an extra long float with double the digits for precision. They offer a 64 bit / 8byte chunk of machine code that encodes 15-16 decimal digits of precision.
Decimals
I'll do it again
-r/dankmemes
Basically an extra extra long float with double a doubles digits of precision. It's only seen in a small number of languages. God help you if you are in need of this data type.