Nodes
Nodes are a basic data structure composed of two parts:
- The data in the node (this can be any variable)
- Links to other nodes
Larger Structures
Nodes can be used to create larger data structures such as linked lists, graphs and trees. You can traverse these structures by going form one node to another by looking at the nodes they point to.
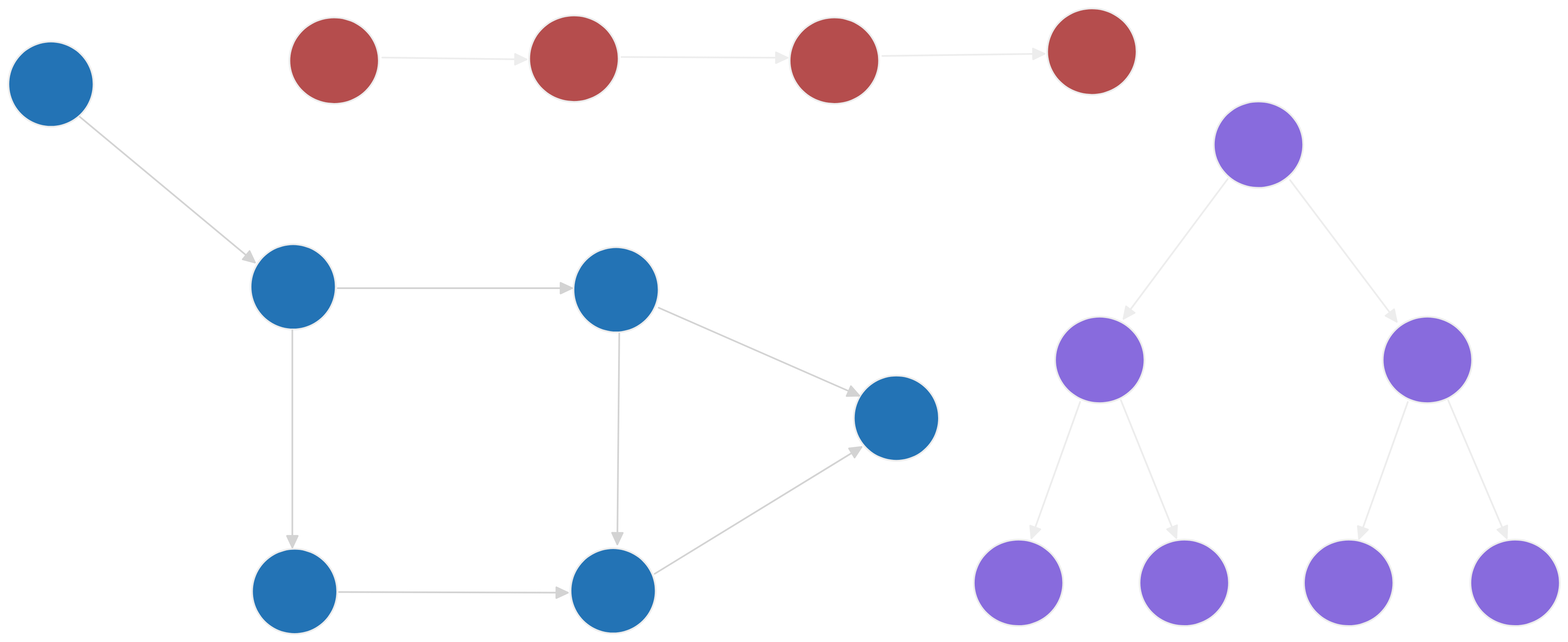
Making Your Own
Node Class
A fairly simple implementation for a structure like a linked list might look like the following:
class Node:
def __init__(self, data, next_node=None):
self.data = data
self.next_node = next_node
def set_next_node(self, next_node):
self.next_node = next_node
def get_next_node(self):
return self.next_node
def get_data(self):
return self.data
This implementation allows you to have a node that only points to the next node in the linked list.
Linking Nodes
This can be done by creating an instance of the node and assigning data to the node.
node1 = Node(1)
node2 = Node(2)
node3 = Node(3)
Then we need to link node1 to node2 and node2 to node3.
node1.set_next_node(node2)
node2.set_next_node(node3)
Traversing the Linked List
To traverse the linked list and print the values, you can start at node1 and follow the next_node references:
current_node = node1
while current_node:
print(current_node.get_value())
current_node = current_node.get_next_node()
1
2
3
There are more in-depth implementations shown in each data structure.